특성공학과 규제
Ridge, Lasso 맛보기
특성공학 (Feature Engineering)
- 특정 애플리케이션에 가장 적합한 데이터 표현을 찾는 것
- 데이터 n개를 다양한 방법으로 활용한다
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
#데이터 셋
df = pd.read_csv('https://bit.ly/perch_csv_data')
# 농어의 길이, 높이, 너비
perch_full = df.to_numpy()
# 농어의 무게
perch_weight = np.array(
[5.9, 32.0, 40.0, 51.5, 70.0, 100.0, 78.0, 80.0, 85.0, 85.0,
110.0, 115.0, 125.0, 130.0, 120.0, 120.0, 130.0, 135.0, 110.0,
130.0, 150.0, 145.0, 150.0, 170.0, 225.0, 145.0, 188.0, 180.0,
197.0, 218.0, 300.0, 260.0, 265.0, 250.0, 250.0, 300.0, 320.0,
514.0, 556.0, 840.0, 685.0, 700.0, 700.0, 690.0, 900.0, 650.0,
820.0, 850.0, 900.0, 1015.0, 820.0, 1100.0, 1000.0, 1100.0,
1000.0, 1000.0]
)
#세트 분리
train_input, test_input, train_target, test_target = train_test_split(
perch_full, perch_weight, random_state=42
)
train_input.shape, test_input.shape, train_target.shape, test_target.shape # ((42, 3), (14, 3), (42,), (14,))
#데이터 특성 변환
poly = PolynomialFeatures(include_bias = False)
poly.fit(train_input)
train_poly = poly.transform(train_input)
train_poly.shape # (42, 9)
#데이터 변환식 알아보기
poly.get_feature_names_out()
# array(['x0', 'x1', 'x2', 'x0^2', 'x0 x1', 'x0 x2', 'x1^2', 'x1 x2', 'x2^2'], dtype=object)
#모형 학습
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(train_poly, train_target)
#모형 평가
print(lr.score(train_poly, train_target))
print(lr.score(test_poly, test_target))
# 0.9903183436982124
# 0.9714559911594134
#최적 Degree 체크하기
for idx in range(2,5):
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree = idx ,include_bias = False)
poly.fit(train_input)
train_poly = poly.transform(train_input)
test_poly = poly.transform(test_input)
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(train_poly, train_target)
print("Degree :", idx)
print(lr.score(train_poly, train_target))
print(lr.score(test_poly, test_target))
print('-'*30)
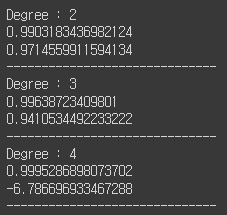
- 최적의 Degree : 2
규제 (Regularization)
- 훈련 세트를 과도하게 학습하지 않도록 하는게 목표
- ex)선형회귀에서 기울기의 크기를 조절
- https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler.html#sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
ss = StandardScaler() # 표준점수
ss.fit(train_poly)
train_scaled = ss.transform(train_poly)
test_scaled = ss.transform(test_poly)
Ridge회귀와 Rasso회귀
- Ridge : 계수를 제곱한 값을 기준으로 규제를 적용
- Rasso : 계수의 절댓값을 기준으로 규제를 적용
Ridge regression
- 릿지 회귀서는 alpha값 조정을 통해 계수를 규제한다. -> Hyperparameter tuning
- alpha값이 크면 규제강도는 강해짐
- alpha값이 작으면 규제강도는 약해짐
- https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#ridge-regression-and-classification
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
train_score = []
test_score = []
alpha_values = [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000]
for alpha in alpha_values:
# 릿지 모델
ridge = Ridge(alpha=alpha)
ridge.fit(train_scaled, train_target)
#훈련 점수와 테스트 점수를 저장
train_score.append(ridge.score(train_scaled, train_target))
test_score.append(ridge.score(test_scaled, test_target))
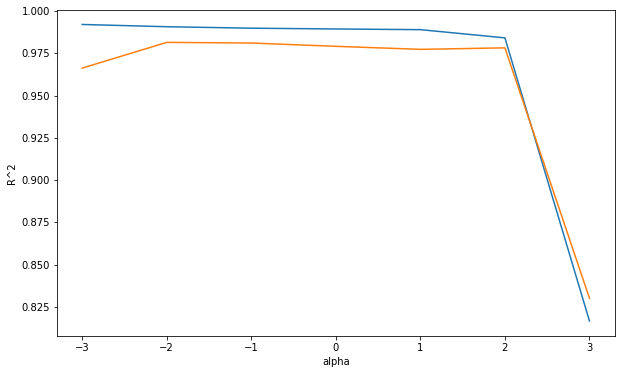
print(train_score)
print(test_score)
# print 결과
# [0.9921179995322787, 0.9907820655909816, 0.9899155822286942, 0.9894514463415389, 0.9890477554300571, 0.9841899617371359, 0.8166954153856678]
# [0.9662956762305547, 0.9815218258396902, 0.9811338451626767, 0.9791864810411214, 0.9773974391100971, 0.9782834538876887, 0.8301276068074791]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
ax.plot(np.log10(alpha_values), train_score)
ax.plot(np.log10(alpha_values), test_score)
ax.set_xlabel('alpha')
ax.set_ylabel('R^2') # 결정계수
plt.show()
Lasso regression
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
train_score = []
test_score = []
alpha_values = [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1,10, 100]
for alpha in alpha_values:
# 라쏘 모델
lasso = Lasso(alpha = alpha)
lasso.fit(train_scaled, train_target)
#훈련 점수와 테스트 점수를 저장
train_score.append(lasso.score(train_scaled, train_target))
test_score.append(lasso.score(test_scaled, test_target))
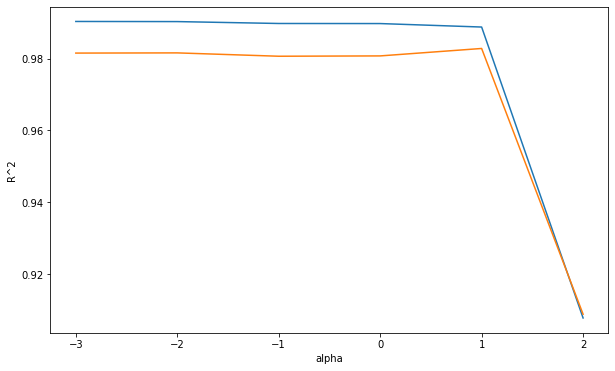
print(train_score)
print(test_score)
# print 결과
# [0.9903086779971262, 0.9902742043357534, 0.9897467764402788, 0.9897257133527957, 0.9887592776354638, 0.9078632215395902]
# [0.9815173499283897, 0.9815706024716399, 0.9806397142575252, 0.9807312585547884, 0.9827993522166355, 0.9089070271410746]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
ax.plot(np.log10(alpha_values), train_score)
ax.plot(np.log10(alpha_values), test_score)
ax.set_xlabel('alpha') # 라쏘회귀 규제의 강도
ax.set_ylabel('R^2') # 결정계수
plt.show()

Leave a comment